
 Your expert partner in CAE simulation
Your expert partner in CAE simulation

Statics and dynamics
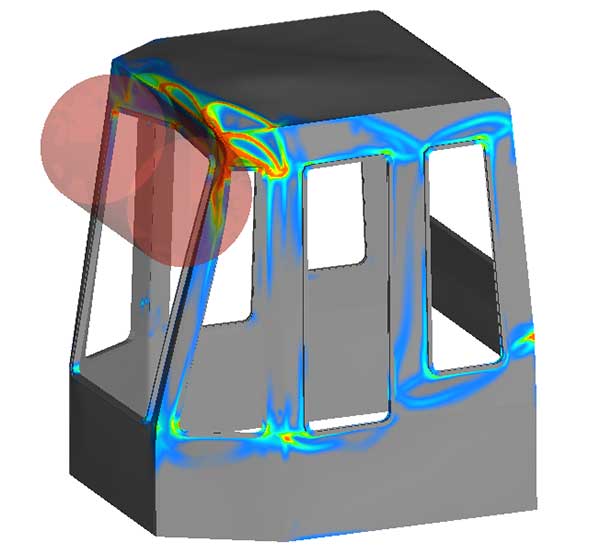 Classical FEA (finite element analysis), i.e. calculation applying the finite element method, mainly serves for strength calculation and deals with static and quasi-static problems. Using the approach of smallest deformations with material and contact formulations that are mostly linear, FEA determines stresses and deformations of structures or machine components due to static or dynamic loading. These analyses allow for a purposive constructive design and optimization of structures, components, and products.
Classical FEA (finite element analysis), i.e. calculation applying the finite element method, mainly serves for strength calculation and deals with static and quasi-static problems. Using the approach of smallest deformations with material and contact formulations that are mostly linear, FEA determines stresses and deformations of structures or machine components due to static or dynamic loading. These analyses allow for a purposive constructive design and optimization of structures, components, and products.
In addition to structural mechanics, FEA also includes modal and eigenfrequency analysis, as well as NVH (noise, vibration, harshness) in vehicle construction.
Analyses of statics and dynamics generally use implicit simulation codes. Nonetheless, explicit methods offer advantages in certain cases of static and dynamic challenges, too.
Crash and short-time dynamics
Explicit CAE calculation and crash simulation also bases on the finite element method but focuses on highly transient and highly dynamic processes. Such scenarios of short-time dynamics occur in accidents or in machine breakdowns, for example. Crash simulation enables the detailed analysis of cause and effect of these rather complex sequences.
In addition to the depiction of highly dynamic processes, explicit simulation has its strength in the handling of complex contact situations, that is to say in the mapping of the diverse interactions of the varied components.
Besides non-linear contact situations another highly non-linear effect arises from the materials’ properties. Exceeding the linear-elastic range of the materials, explicit simulation enables the capturing of their non-linear, plastic stress-strain behaviour, even considering further complex properties, such as strain-rate dependency, dynamic hardening, triaxiality and temperature dependency. Beyond the linear-elastic range of static analyses, these approaches allow for an examination of complex and highly non-linear loading of structures and of their deformation and failure behaviour up to rupture.
Some typical examples for the use of explicit simulations are automotive crash tests, containment safety of turbomachines, and drop tests as well as forming processes. In the case of high non-linearity in quasi-static problems, explicit instead of implicit simulation is useful, too.
For the diverse calculations and simulations we apply the following programs:
- LS-Dyna, Abaqus, Radioss, PAM-Crash
- Nastran, LS-Dyna, Abaqus, Ansys
In LS-Dyna in particular, the intense application for many years enables us to efficiently solve our customers’ tasks and so to share the benefit of our high expertise.
Kontakt
INPROSIM GmbH
Birkenweg 1
64354 Reinheim
Germany
+49 (0) 61 62 / 65 23
www.inprosim.de
info@inprosim.de
Kontakt
INPROSIM GmbH
Birkenweg 1
64354 Reinheim
Germany
+49 (0) 61 62 / 65 23
www.inprosim.de
info@inprosim.de